Molecular-biological methods of research and their use
Molecular biological methods of researchplay a big role in modern medicine, criminalistics and biology. Thanks to advances in the field of DNA and RNA studies, a person is able to study the genome of the organism, identify the causative agent of the disease, recognize the desired nucleic acid in a mixture of acids, etc.
Molecular biological methods of investigation. What it is?
As far back as the 1970s and 1980s, scientistsdecipher the human genome. This event gave impetus to the development of genetic engineering and molecular biology. The study of the properties of DNA and RNA led to the fact that now it is possible to use these nucleic acids in order to diagnose the disease, to study genes.
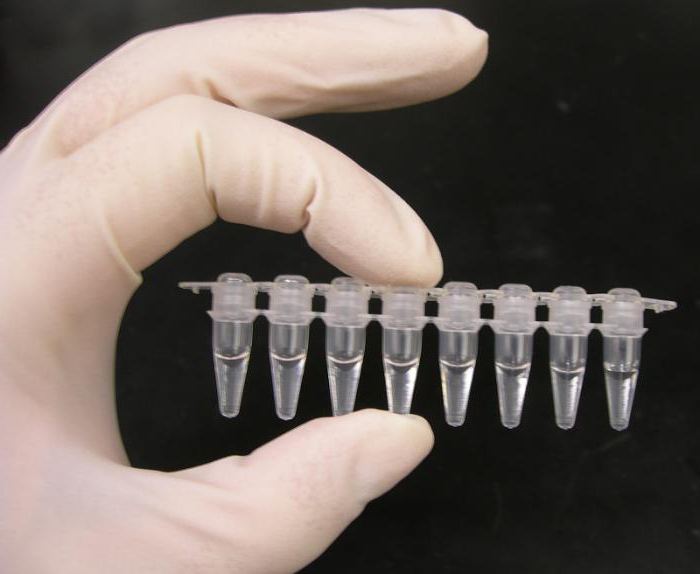
Preparation of DNA and RNA
Molecular biological methods of diagnosisrequire the presence of starting material: more often it is nucleic acids. There are several ways to isolate these substances from the cells of living organisms. Each of them has its advantages and disadvantages, and this must be taken into account when choosing the method of isolation of nucleic acids in pure form.
1. Preparation of DNA according to Marmur. The method consists in treating the mixture of substances with alcohol, as a result of which pure DNA precipitates. The disadvantage of this method is the use of aggressive substances: phenol and chloroform.
2. DNA isolation by Boom. The basic substance used here is guanidine thiocyanate (GuSCN). It promotes the deposition of deoxyribonucleic acid on specialized substrates, from which it can subsequently be collected with a special buffer. However, GuSCN is an inhibitor of PTC, and even a small part of it, trapped in the precipitated DNA, can affect the course of the polymerase chain reaction, which plays an important role in the work with nucleic acids.
3. Precipitation of impurities. The method differs from the previous ones in that not the molecules of the deoxyribonucleic acid themselves are precipitated, but impurities. To do this, use ion exchangers. The disadvantage is that not all substances can precipitate.
4. Mass screening. This method is used in those cases when precise information on the composition of the DNA molecule is not needed, but it is necessary to obtain some statistical data. This is due to the fact that the structure of the nucleic acid can be damaged by treatment with detergents, in particular, with alkalis.

Classification of research methods
All molecular biological methods of research are divided into three large groups:
1. Amplification (using a variety of enzymes). This includes PCR - polymerase chain reaction, which plays a large role in many of the diagnostic methods.
2. Non-appellation. This group of methods is directly related to the operation of mixtures of nucleic acids. Examples are 3 types of blotting, in situ hybridization, etc.
3. Methods based on recognition of a signal from a probe molecule that binds to a specific DNA or RNA probe. An example is a hybridization system in a Hybrid Capture System solution (hc2).
Enzymes that can be used in molecular biological methods
Many methods of molecular diagnostics involve the use of a wide range of enzymes. Below are the most commonly used:
1. Restrictase - "cuts" the DNA molecule into the necessary parts.
2. DNA polymerase - synthesizes a double-stranded molecule of deoxyribonucleic acid.
3. Reverse transcriptase (revertase) - used to synthesize DNA on the RNA matrix.
4. DNA ligase - responsible for the formation of phosphodiester bonds between nucleotides.
5. Exonuclease - removes nucleotides from the end sections of the molecule of deoxyribonucleic acid.

PCR is the main way to amplify DNA
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is activeis used in modern molecular biology. This is a method in which a huge number of copies can be obtained from a single DNA molecule (amplify molecules).
The main functions of PCR are:
- diagnostics of diseases;
cloning of DNA and genes.
To carry out polymerase chain reactionthe following elements are required: the original DNA molecule, the thermostable DNA polymerase (Taq or Pfu), the deoxyribonucleotide phosphate (sources of nitrogen bases), the primers (2 primers per DNA molecule) and the buffer system itself, in which all reactions are possible.
PCR consists of three stages: denaturation, annealing of primers and elongation.
1. Denaturation. At a temperature of 94-95 degrees Celsius, the breaking of the hydrogen bonds between the two DNA strands continues, and as a result we get two single-chain molecules.
2. Annealing of the primers. At a temperature of 50-60 degrees Celsius, primers are attached at the ends of single-stranded nucleic acid molecules by the type of complementarity.
3. Elongation. At a temperature of 72 degrees, the synthesis of daughter double-stranded molecules of deoxyribonucleic acid occurs.

DNA sequencing
Molecular biological methods of researchoften require knowledge of the sequence of nucleotides in a molecule of deoxyribonucleic acid. Sequencing is used to determine the genetic code. Molecular diagnostics of the future will be based on knowledge obtained in determining the sequence of a person.
The following types of sequencing are distinguished:
- sequencing by Maxam-Gilbert;
- sequencing by Sanger;
- pyrosequencing;
- nanoporous sequencing. </ ul </ p>