Fetal position and its types
At an early pregnancy, when a lotfree space in the uterus, the fetus does not have any specific position. He is not limited in his movements, turns and turns around, as you like and as many as you like.
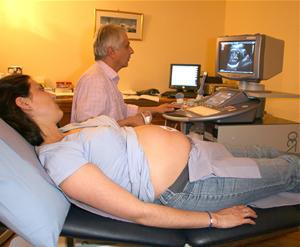
As a rule, the most common isPreposition, which is characterized by the coincidence of the longitudinal axes of the uterus and the baby. However, sometimes there is an incorrect position of the fetus, at which its axis crosses the uterine at some angle. Depending on the peculiarities of this angle, several types of incorrect presentations are distinguished, which most often arise due to the narrow pelvis of the mother, low attachment of the placenta, tumors of the uterus and other genital organs, as well as a reduced tone of the abdominal or uterine wall and polyhydramnios.
Now let's talk about the types of presentations in more detail.
Thus, the occipital position of the fetus is determined withthe use of vaginal examination, as well as when examining the gynecologist and ultrasound data. If the occipital presentation in the anterior position, then this is considered the most favorable condition for conducting natural childbirth. In other cases, they are possible if the pelvis is of normal size, and the head of the fetus is small. It is very important to diagnose the rear and transverse position in time to take action before the second stage of labor has begun. Doctors in this case change the position of the fetus by hand, adjusting the position of the parturient woman. If there is a transverse occipital position of the fetus, then the turn, as a rule, occurs afterwards spontaneously.
Frontal presentation is formed as a result ofpartial extension of the head. Most often this situation goes either to the occipital or to the facial. However, if the mother has a narrow pelvis, this becomes impossible, and doctors prohibit the delivery of births naturally.
At the normal size of the pelvis, if observedfacial position of the fetus, normal delivery, on the contrary, are possible. If the position is rear, the doctor independently turns the child. In case of failure, a caesarean section is prescribed.
Pelvic presentation can only be diagnosedafter a gynecological examination, the results of ultrasound and vaginal examination. Most often, this situation arises as a result of disproportionate uterus and the size of the child. In the presence of a similar pathology, the risk of anomalies is approximately 6.5%. Doctors can allow the delivery of births in a natural way only under the condition of a purely breech presentation, the weight of the fetus is 2800-3500 g, the normal pelvis is in the mother, the head of the fetus is not re-expanded. In such circumstances, the risk of birth injury is approximately 3%. Otherwise, a caesarean section is administered.
The transverse position of the fetus is determined only by ultrasoundand external gynecological examination. Most often, a similar diagnosis occurs in women who have given birth several times, as well as with preterm labor, the presence of uterine fibroids, placenta previa and multiple pregnancies. If there are no contraindications, at about the end of the 37th week an attempt is made to manually rotate the fetus to the head. When such a diagnosis is made directly during childbirth, a cesarean section is prescribed. To reduce the risk of injury to the mother and child, the incision is longitudinal. Very often, when the outflow of amniotic fluid is carried out, the transverse position of the fetus provokes the prolapse of the umbilical cord.
If the presentation is mixed, and the headis below the small presenting part, births are allowed naturally. In other cases, an attempt is made to turn: if the process is unsuccessful, surgical intervention by caesarean section is prescribed.