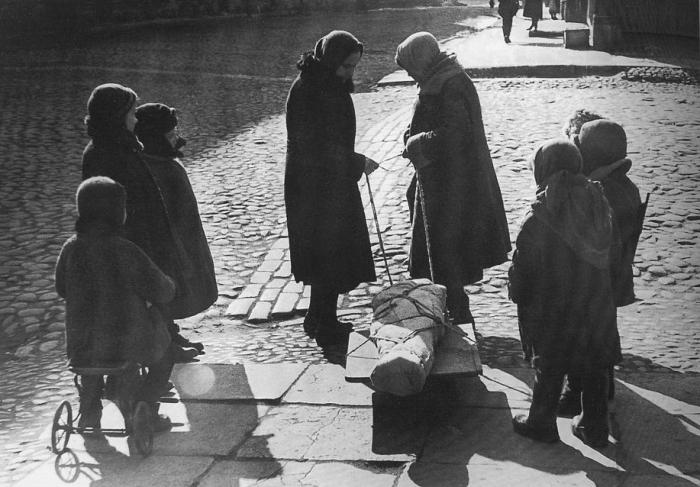
What is the road of life in the blocked Leningrad?
The transport highway, which took place inThe time of the Great Patriotic War through Ladoga, rightly called the Road of Life. Since the autumn of 1941 through the winter of 1943, it was almost the only way to the blocked Leningrad, where the food was sorely lacking. More details on what is the Road of Life, you will learn from this article.
The beginning of the blockade
The blockade of the city-hero of Leningrad began 8September 1941, when the German troops closed the circle of encirclement, taking Shlisselburg. It was through this city that the last route passed, which connected Leningrad with the Soviet Union. Therefore, only the winter and ice of Lake Ladoga was the last hope to save the inhabitants from starvation.
First deliveries to the hungry
It should be noted that the reservoir had very complexnavigation conditions, and all the ways of supply were built around the Ladoga. On the shores of the lake, no pier or pier was equipped. But this did not stop the commanders from starting to supply food in September. The route of the Road of Life passed from Volkhov to Novaya Ladoga and then along the water to the Osinovets lighthouse. In the middle of September, the first two barges came here, on the decks of which there were more than 700 tons of grain and flour. Since then the date of September 12th is considered to be the day when Ladoga Life Road began to work. Only until the end of 1941, about 60 thousand tons of various cargoes were delivered to the distressed city and 33.5 thousand people were evacuated. The basis of all cargo transported along the Road of Life was forage, food, fuel and ammunition. Various heroic events are rich in the Great Patriotic War, the blockade of Leningrad and the equipment of the Road of Life, perhaps - one of the most important.

The road of life
Food, medicine and ammunition are notenough. The problem was to be solved by the Road of Life (on ice passing). At the end of November, Soviet spies conducted a total reconnaissance of the lake and the future highway, and on November 20 the first convoy headed by Lieutenant M. Murov set off on the ice from Vaganovsky descent to Leningrad. 63 tons of flour were loaded on 350 sledges. Already on the morning of November 21 the convoy arrived at the place, which justified the operation and clearly gave the command to understand what the Road of Life is for supplying the Leningraders.
The next day in the blocked city wassent 60 loaded cars GAZ-AA ("polutorok"), the transportation was commanded by Captain V. Porchunov. The road to life in the war earned full power, only for the first winter, 360 thousand tons of cargo were transported, of which 260 thousand - food. Cars, returning to the Greater Land, necessarily took the body of the city's population, evacuating in the first year of the blockade about 550 thousand people. Thanks to systematic transportation, the norms for the delivery of food in Leningrad increased and the population began to starve less.

A new stage of supply
The next stage of navigation on Lake Ladogabegan at the end of May 1942, cargo ships transported more than 1 million cargos in both directions, of which 700,000 were in Leningrad. 445 thousand people from the civilian population were evacuated to the Greater Land. In the opposite direction, about 300,000 troops were delivered to the front.
The summer of the 42nd made it possible to lay a pipeline on the bottom of Ladoga, which allowed to supply the city with fuel, and a cable for supplying electricity from the Volkhov hydroelectric power station.
From the middle of December 1942 to March 1943, againThe already-legendary Road of Life began to operate. During this period more than 200 thousand various cargoes were transported and 100 thousand people were evacuated.
On January 18, 1943, the Red Army won thethe enemy Shlisselburg, and the blockade of Leningrad was broken. Immediately after this event, a railway was laid, along which all the necessary cargoes went without any problems. Subsequently, this road was named the Victory Road. But, despite this, the Ladoga route continued to operate until the final blockade of the city, that is, until January 1944.

Route Description
Answer the question: "What is the Way of life?"Is impossible without a thorough description of its route. It began at the Finnish railway station and by land followed the shore of Ladoga, and then directly over the frozen lake. At the same time, the main route of the Road of Life passed only 25 kilometers from enemy positions on the shore, from where the firing of moving convoys was carried out. Drivers of laden transport constantly risked their lives, moving under the fire of German artillery and aviation and risking falling into the ice of the lake. But, despite all the difficulties, on the road every day there were from five to eight tons of different cargo.

During the use of the legendary road,a curious fact is established: the worst thing in the implementation of the movement on the ice is not the raids of German bombers, but the movement with a resonant speed. In this situation, any passenger car went under the ice in the place where a heavily loaded convoy had passed several hours ago. Therefore, the speed of movement on each section of the lake was strictly regulated.
The further destiny of the Road of life
As is known, in the spring of 1943, when the ringthe blockade of Leningrad was broken off, the road of life was replaced by a new Victory Road, which was a branch line from the Volkhov to Leningrad. But in winter, food was delivered to the city on the old route - through Lake Ladoga.

The Great Patriotic War, the blockade of Leningrad inin particular, are vivid examples of sincere patriotism and fortitude of the spirit. Millions of people did not surrender to the enemy and suffered all the hardships and difficulties of the war years. What is the Way of Life? This is one of the many exploits of the Soviet people in the war years.