Ovarian hypofunction, symptoms and treatment
Ovarian hypofunction meansa clinical term that includes diseases that differ in pathogenesis and etiology. All of them have similar signs of sexual underdevelopment. These include infertility, hypoplasia, amenorrhea, hypoestrogeny and hypotrophy of the uterus and ovaries.
There are many varieties of primaryhypofunction. The primary, primary, clinical form of this disorder is premature menopause. Usually it develops in women older than 35 years. In the etiology of the disease, the main role is played by various negative environmental factors. The cause of the disorder can be gene mutations, hereditary predisposition, autoimmune disorders in the ovaries.
Ovarian hypofunction can occur in the backgroundnormal generative and menstrual functions. It manifests itself in the form of tides to the head, amenorrhea, excessive sweating, rapid fatigue, weakness, pain in the heart and head, reducing efficiency. During the onset of the disorder, they determine: a reduced size of the uterus and ovaries, a low concentration of prolactin and estrogens, the absence of follicles and yellow bodies, an increased content of follicle-stimulating and luteinizing hormones in the blood. This ovarian hypofunction has such treatment: the use of hormonal drugs (estrogen-progestogen and estrogen). Hormonal therapy significantly improves the condition of such patients, so when establishing this diagnosis, it is necessary to begin treatment immediately.
Isolated (secondary) hypofunction of the ovaries,organic and functional disorders of the hypothalamic-pituitary system are important clinical forms of such a disorder. Despite the fact that the ovaries are completely normal number of follicles, they do not occur the process of ripening. For such a condition are inherent: hypotrophy, primary or secondary amenorrhea, hypoplasia of the uterus and ovaries, hypoestrogenia. This hypofunction of the ovaries usually occurs against the background of normal follicle-stimulating and luteinizing hormones in the blood.
There is still a syndrome of polycystic ovaries. About 3% of young women suffer from this disease. This disorder is characterized by excessive production of androgens (in the adrenal and ovaries), glitches in their peripheral metabolism. Along with these signs, an increased amount of luteinizing hormones, a normal or decreased concentration of follicle-stimulating hormone, an increased content of prolactin in the blood is determined. Such ovarian hypofunction, symptoms: characterized by the development of pseudohermaphroditism, which are characterized by hyperandrogenism, clitoral hypertrophy, amenorrhea, infertility, anovulation and severe acne.
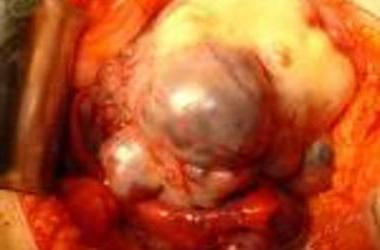
Another reason whyhypofunction of the ovaries may occur, there may be a virilizing tumor of the ovaries. Tumor cells in the ovaries form an excessive amount of testosterone, dehydroepiandrosterone and androstenedione, which are male sex hormones. Clinical manifestations of the disease are lack of menstruation, irregular meager menstruation (oligoopsomenorea), acyclic uterine bleeding. This disease is characterized by the manifestations of alopecia, hirsutism, coarsening of the voice, the formation of the male type, the formation of pseudohermaphroditism, hypertrophy of the clitoris.
If there is ovarian hypofunction, treatmentappointed after a comprehensive survey. When tumors are formed, chemotherapy, radiation and surgical removal of the tumor are performed. Hormonal disorders after a thorough examination are treated with various hormonal drugs.