What is the rectal temperature for ovulation?
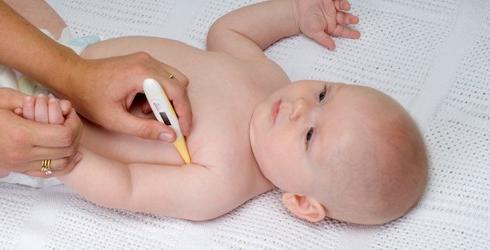
Rectal temperature measurement is usedgynecologists for assessing the woman's reproductive health. More often it is called basal. According to the data obtained, graphs are constructed that help determine the time of ovulation, the presence of hormonal disorders and inflammatory processes in the reproductive tract, as well as the threat of abortion.
On the first day of the cycle, the follicle begins to ripenthe effect of estrogens synthesized in the ovaries. When this process is over, it bursts and an egg leaves it. This ends the first phase of the cycle and the second phase begins.
Then the formation of the yellow body occurs. It synthesizes progesterone. This hormone prepares the endometrium. If pregnancy does not come, then menstruation begins, this ends the second phase.
Estrogens contribute to a decrease in rectaltemperature, and progesterone - its increase. Thus, in the first phase of the cycle it is low, and in the second phase it is high. Immediately before ovulation, a surge of estrogen is observed, which provides an even greater drop in temperature. However, this phenomenon can not always be fixed when it is measured.
Thus, ideally the rectal temperaturewhen ovulation should be the lowest in the chart. And after it should be a jump up. When plotting a plot on the horizontal axis, the days of the cycle are plotted, and along the vertical axis, measurements are plotted.
Many women who build them are interested,what temperature is the norm in ovulation. It depends on the individual characteristics. However, in most women in the first phase, the temperature lies in the range 36.4-36.8, and in the second -37-37.2. Accordingly, at the time of ovulation, it should drop below 36.4.
However, if a woman does not detect this phenomenonyourself on the charts, you should not be upset. Most of those who build them, it faces this. Most often, the temperature during ovulation lies within the first phase.
The most important thing is that the schedule clearlyThe region of low and high temperatures was viewed. The presence of a jump and indicates the occurrence of ovulation. Although this is not always the case. With luteinization of the follicle, progesterone is secreted, a rise in temperature occurs, and there is no ovulation, and, accordingly, pregnancy is impossible.
The fact is that the release of the egg from the mature follicle stimulates a sharp increase in the level of LH. By the way, it is he who fixes the tests for ovulation.
However, in some women the splash occursearlier than necessary or not at all. In this case, the follicle does not burst, ovulation does not occur, and it lutes, existing until the end of the cycle and secreting progesterone. Experts believe that the graph on this can indicate a long rise in the temperature curve (more than 3 days).
Temperature at ovulation, in the first and second phasesmay be different from the quoted norms. This can be an individual feature. A very important difference is the average temperature between phases. The value should exceed 0.4, otherwise this may indicate a lack of progesterone and / or estrogens.
The temperature during ovulation, in the first and second phases,which varies randomly throughout the cycle, may indicate that there is no exit of the matured egg. In this case, the graph resembles a fence, there is no region of high and low temperatures.
The duration of the second phase, which should be more than 10 days, and is better than 14. The high temperature throughout the cycle indicates a large amount of prolactin.
Based on the kind of graphs only, it is impossible to draw definitive conclusions. It is necessary to undergo a hormonal examination, and only then treatment can be prescribed.
Thus, the temperature during ovulation shouldbe the lowest per cycle. However, this does not happen to everyone. The most accurate method of determining the time of ovulation - folliculogenesis in combination with the delivery of hormones.